Plant-Based Protein: Your Beginner’s Guide to a Healthier Diet
Navigating the world of plant-based protein can be simple with the right information; this guide offers an accessible introduction to understanding its benefits, sources, and how to incorporate it into your daily meals for a healthier lifestyle.
Embarking on a journey towards a plant-based diet? Let’s start with **navigating the world of plant-based protein: A comprehensive guide for beginners**. Discover how easy and beneficial it can be to incorporate these protein sources into your daily meals.
Understanding Plant-Based Protein
Plant-based protein is derived from sources like legumes, nuts, seeds, vegetables, and whole grains. It offers an alternative to animal-based protein, catering to vegetarians, vegans, and anyone looking to diversify their protein intake.
Why Choose Plant-Based Protein?
Choosing plant-based protein can offer several health benefits and align with ethical and environmental considerations. It’s a sustainable and nutritious way to fulfill your protein requirements.
Benefits of Plant-Based Protein
Incorporating plant-based proteins into your diet has several benefits beyond just providing essential amino acids. It’s often lower in saturated fat and higher in fiber compared to animal-based sources.
- Supports heart health by reducing cholesterol levels.
- Aids in weight management due to high fiber content.
- Promotes gut health by feeding beneficial gut bacteria.
- Reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes through improved blood sugar control.
These advantages make plant-based protein a valuable addition to any balanced diet, offering both health and environmental benefits.
Ultimately, understanding why plant-based protein is a great choice lays the foundation for incorporating it effectively into your diet, providing a host of health benefits along the way.
Top Plant-Based Protein Sources
Discover the best sources of plant-based protein to include in your diet. This variety ensures you receive a broad spectrum of nutrients and essential amino acids.
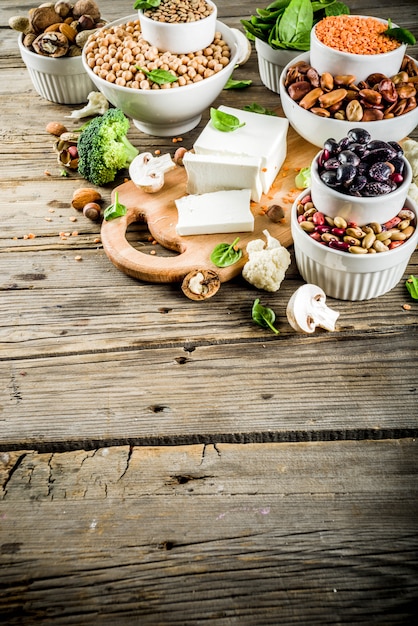

Legumes: The Protein Powerhouses
Legumes, including beans, lentils, and peas, are excellent sources of protein and fiber. They are versatile and can be used in a variety of dishes.
Nuts and Seeds for Protein and Healthy Fats
Nuts and seeds offer a combination of protein, healthy fats, and essential minerals. They are great for snacking or adding to meals.
Including a variety of these protein sources ensures a diverse intake of nutrients. Each offers unique benefits, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Incorporating Plant-Based Protein into Your Diet
Integrating plant-based protein into your meals does not have to be complex. With a few simple strategies, you can easily boost your protein intake.
- Start by swapping meat for legumes in a few meals each week.
- Add nuts and seeds to your breakfast cereal or yogurt.
- Use tofu or tempeh in stir-fries and salads.
Sample Meal Ideas
Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- Breakfast: Tofu scramble with whole-grain toast.
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with chickpeas and vegetables.
- Dinner: Lentil soup with a side of whole-grain bread.
These meals are protein-packed, nutritious, and easy to prepare. Experiment with different recipes to find your favorites!
Ultimately, adapting your meals to include plant-based proteins is a delicious and nutritious way to enhance your overall diet.
Addressing Common Concerns
Many beginners have questions about plant-based protein. Here are some common concerns addressed to help you feel more confident in your choices.
Complete vs. Incomplete Proteins
Unlike animal proteins, some plant-based proteins are considered “incomplete” because they lack one or more essential amino acids. However, eating a variety of plant-based foods throughout the day ensures you get all the necessary amino acids.
Protein Requirements
The recommended daily protein intake varies depending on factors like age, sex, and activity level. Generally, adults need about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Plant-based eaters can easily meet this requirement with a well-planned diet.

Addressing these concerns helps clarify common misconceptions, paving the way for a well-informed and balanced plant-based diet.
Tips for Success
Succeeding with plant-based protein requires a few strategies to ensure you’re getting enough protein and essential nutrients. Here are some tips to get you started:
Plan Your Meals
Planning your meals ahead of time can help you ensure you’re getting a balanced intake of protein and other essential nutrients. Use meal planning apps or create a weekly menu to stay on track.
Read Labels Carefully
When buying plant-based protein products, read the labels carefully to check for added sugars, sodium, and unhealthy fats. Choose products with minimal processing and simple ingredient lists.
Staying committed to these tips will help you maintain a balanced and healthy plant-based diet, ensuring you receive all the essential nutrients you need.
The Environmental Impact of Plant-Based Protein
Choosing plant-based protein is also an environmentally responsible decision. Plant-based diets generally have a lower environmental footprint compared to diets that rely heavily on animal products.
Sustainability
Plant-based agriculture typically requires less land, water, and energy than animal agriculture. This makes plant-based protein a more sustainable option for feeding a growing global population.
Reducing Your Carbon Footprint
By reducing your consumption of animal products, you can significantly lower your carbon footprint. Plant-based diets contribute less to greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation.
Recognizing the environmental advantages of plant-based protein reinforces the idea that dietary choices can have a significant positive impact on the planet.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🌱 Protein Sources | Legumes, nuts, seeds, and tofu are excellent plant-based protein options. |
| ❤️ Health Benefits | Plant-based protein supports heart health, aids in weight management, and promotes gut health. |
| 🌍 Environmental Impact | Plant-based diets reduce carbon footprint and are more sustainable. |
| 🍳 Meal Planning | Plan meals and read labels to maximize nutrient intake and avoid unhealthy additives. |
What are the best plant-based protein sources?
▼
Legumes like lentils and beans, nuts, seeds such as chia and flax, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa are all excellent sources of plant-based protein. Incorporate a variety for a balanced amino acid profile.
▼
The recommended daily protein intake varies, but generally, adults need about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Ensure a balanced diet with diverse protein sources to meet this need.
▼
Yes, quinoa and soy products are complete proteins. By combining different plant-based foods, you can also get all essential amino acids. Variety is key to a complete protein profile.
▼
Start by swapping meat for legumes in a few meals each week. Add nuts and seeds to your breakfast. Use tofu or tempeh in stir-fries and salads for an easy protein boost.
▼
Plant-based diets have a smaller environmental footprint than diets with animal products. They require less land, water, and energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation significantly.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of plant-based protein is a journey towards better health and a more sustainable planet. By understanding the sources, benefits, and practical tips, you can easily incorporate plant-based protein into your diet, making a positive impact on both your well-being and the environment.





